The Latest in Clean Energy News
News, analysis and opinion covering the renewable energy
Latest news on green tech and green energy


When it comes to supplying the world's energy needs, solar energy is becoming more and more popular because of its many benefits. Sustainability is among its most important advantages. Sunlight, which is plentiful and boundless in terms of human time, is the source of solar energy, a renewable resource. In stark contrast, fossil fuels are limited resources that worsen the environment.
Reducing electricity costs is one of solar energy's main advantages. Property owners and companies can generate their own electricity and save their monthly utility bills by installing solar panels, which lessens their dependency on the grid. Solar installations are made even more financially attractive in many areas by tax rebates and government incentives.

When it comes to supplying the world's energy needs, solar energy is becoming more and more popular because of its many benefits. Sustainability is among its most important advantages. Sunlight, which is plentiful and boundless in terms of human time, is the source of solar energy, a renewable resource. In stark contrast, fossil fuels are limited resources that worsen the environment.
Reducing electricity costs is one of solar energy's main advantages. Property owners and companies can generate their own electricity and save their monthly utility bills by installing solar panels, which lessens their dependency on the grid. Solar installations are made even more financially attractive in many areas by tax rebates and government incentives.






⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“great site”
⭐⭐⭐⭐
“This option can be used to attach arbitrary domain-specific data to a constraint. The configured payload is not used by the Validator component, but its processing is completely up to you.”
⭐⭐⭐
“Site may be some better...”
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Twenty years ago I bought city sewage from the Authority, sterilized and processed it myself and made a profit on a crop.”
⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Over a million square miles of crop- and stock-bearing land was affected, from southern Victoria to the waist-high Mitchell grasslands of the Northern Territory.”
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“Peter Mill distributes his surplus pecan crop as food for livestock through a local co-op.”
⭐⭐⭐
“Bob and the boys were pleased with his work and seemed to get along well with him; apparently he hadn't a lazy bone in his body, according to Bob.”
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
“It was spotlessly clean, with short cropped hair trimmed close to its head with clippers. It was a little boy.”

Energy from renewable natural resources is defined as that which replenishes as quickly as it is used up. Renewable energy uses the force of natural phenomena like sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat to generate energy instead of fossil fuels, which have a limited supply and can take millions of years to create. Because of this, it is a sustainable substitute that can greatly lessen our dependency on finite resources.
In the struggle against climate change, the value of renewable energy has grown more and more apparent. A workable way to lower carbon footprints and lessen environmental effects is through the use of renewable energy, while greenhouse gas emissions from human activity—mainly the burning of fossil fuels—continue rising. We can improve public health, reduce air pollution, and support international efforts to achieve net-zero emissions by switching to greener energy sources.
Renewable energy technologies come in a variety of forms these days, each with special qualities and uses. While hydropower uses flowing water to generate electricity, biomass turns organic materials into fuel, geothermal energy uses the heat from the Earth's interior, wind energy uses the kinetic energy of the wind through turbines to capture sunlight. When we comprehend these various kinds, we may acknowledge their combined potential to build a more sustainable future while also appreciating their individual advantages and difficulties.
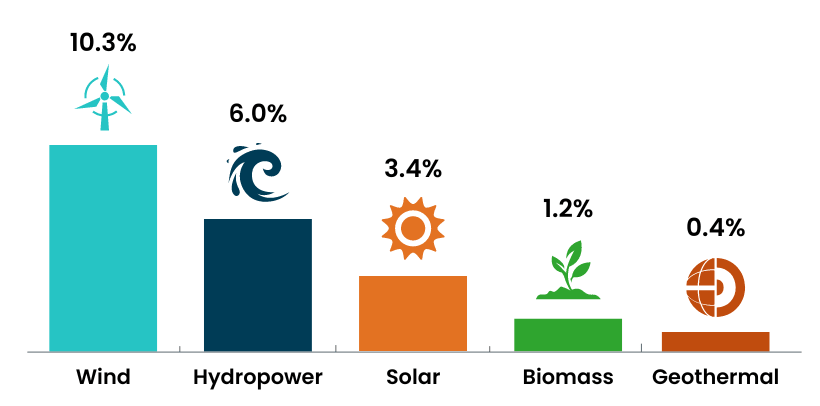
Now, more than 20% of the electricity produced in the United States comes from renewable sources. The percentages of all electricity produced in 2022 that will come from each type of renewable energy are shown in the following graphic:
With its ability to produce heat and electricity from the sun's enormous power, solar energy is one of the most promising renewable energy sources. Essentially, using a variety of technologies, solar energy systems transform sunlight into useful energy. Using solar panels, the most popular technique, sunlight is directly converted into electricity through the use of photovoltaic (PV) cells. Electric current that can be used for home or business purposes is produced when sunlight strikes these cells, exciting electrons.
PV and solar thermal systems are the two main categories of solar technologies. The use of semiconductor materials in photovoltaic systems allows for the widely known generation of power from sunshine. Due to their versatility for many uses, these systems can be deployed on rooftops or in enormous solar farms. Nevertheless, the goal of solar thermal technology is to harness solar radiation to create steam or hot water. In industrial procedures or residential situations where high temperatures are necessary, this approach works especially well for heating.
Beyond its benefits to the environment, solar energy has other perks. The sustainability of sunshine is a major benefit; unlike fossil fuels, it provides an endless supply. That means we can use renewable energy without using up too many natural resources as long as the sun shines. Since they require little upkeep and don't require fuel, solar panels usually have low operating costs once installed. When combined, these result in significant energy bill savings and help lower greenhouse gas emissions.
An effective strategy to satisfy our expanding energy needs responsibly is to utilize solar energy using PV and thermal technologies. Solar power is one of the main contenders in the shift to a greener future because of its many benefits, which include economic savings and environmental sustainability.
With its ability to harness the power of wind through advanced technology, wind energy is one of the most promising renewable energy sources. Wind turbines, which transform wind kinetic energy into mechanical energy and ultimately into electricity, are the central component of this process. Turbine blade rotation is triggered by wind flow. Power generated by the turbine's internal generator is spun by this rotation and can be used locally or supplied into the grid. Wind turbines of today are a practical choice for both rural and urban environments because of their ability to increase efficiency and reduce noise.
Offshore and onshore wind farms are the two primary varieties that exist. When it comes to efficiently capturing wind, onshore wind farms are usually situated on land and comprise several turbines dispersed over large areas. Though there are advantages to less expensive construction and simpler maintenance, these installations could encounter difficulties such conflicts with other land uses and issues with visual effect. Conversely, offshore wind farms are located in areas of water with stronger and more reliable wind patterns. Offshore farms provide substantial advantages in terms of potential energy generation, even if their installation requires more capital due to the severe marine environment and complications involved.
Beyond its potential to produce clean electricity, wind energy offers other benefits. Due to its renewable nature, this resource greatly aids in the fight against climate change as it emits no greenhouse gases when in use. Jobs have been created in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research, among other sectors, as a result of the wind energy industry's expansion. As a result of creating new job possibilities in the communities surrounding both onshore and offshore locations, the switch to sustainable energy sources like wind power also helps local economies and advances environmental goals.
Among the many advantages wind energy provides, like lower carbon emissions and increased economic growth through job creation, it is particularly noteworthy as a method of harnessing the breeze from nature. The prospects for this dynamic industry within the renewable energy landscape appear promising as technology progresses and public policy continues to favor renewables.
Utilizing the kinetic energy of falling or flowing water, hydropower is one of the most well-known and traditional sources of renewable energy. It produces electricity on demand. To create a reservoir that can hold water, this technique usually entails building a dam on a river. The water's potential energy is transformed into mechanical energy and then electrical energy as it travels through turbines after being released from the reservoir. By controlling the supply of electricity according to demand, this technology not only gives a consistent source of power but also a great deal of flexibility.
Hydraulic systems can be classified into two main categories: storage and run-of-river. Rivers can be used in run-of-river systems without having their route or level drastically changed. These systems don't need big reservoirs, thus their environmental effect is usually minimal. However, the amount of electricity they generate varies based on seasonal river flows. In storage hydropower systems, however, large reservoirs are created by the construction of dams. These establishments are more dependable for steady power production since they have the capacity to store vast amounts of water, which permits controlled release during periods of high electrical demand.
Reliability as an energy source is one of the primary benefits of hydropower. Hydropower's capacity to efficiently control water flow makes it a reliable energy source, in contrast to solar or wind power, which might fluctuate depending on the weather. With over 90% of the energy in flowing water converted into useful electricity, modern hydroelectric plants tout exceptional efficiency rates. Ancillary services like load balancing and frequency regulation are provided by hydropower, which helps maintain grid stability.
Correct management of hydropower yields major environmental benefits in addition to its efficiency and dependability. It is an important factor in lowering carbon footprints worldwide and emits fewer greenhouse gases than fossil fuels. In addition to creating jobs in the building and maintenance industries, many hydro projects include fish ladders and other safeguards for aquatic environments, which boost local economies.
The capacity of hydropower to provide consistent, effective power while simultaneously making a beneficial contribution to sustainable development objectives makes it a powerful force in the renewable energy scene. Hydropower is a vital component of our shift to greener energy sources because of its capacity to expand resources as infrastructure and technology develop.
A dependable and long-lasting energy source, geothermal energy uses the inherent heat that the Earth's crust naturally stores. Steam or hot water from subterranean reservoirs is used in geothermal plants to produce energy. Deep wells are drilled into geothermal deposits, which can have temperatures as high as several hundred degrees Celsius, to start the process. This hot water or steam is accessible, brought to the surface, and utilized to power turbines that are connected to generators, so transforming thermal energy into electrical energy.
The two main categories of geothermal systems are flash steam and dry steam. The earliest kind of geothermal power generation are dry steam plants, which use steam extracted directly from geothermal reservoirs to drive turbines. As the water's pressure drops as it approaches the surface, high-pressure hot water from below is allowed to "flash" into steam in flash steam plants. Later, turbines that produce power are driven by this quickly growing steam. Some systems use binary cycles to move heat from geothermal fluids to a lower boiling point secondary fluid. The secondary fluid then vaporizes and turns a turbine without releasing any geothermal fluids into the atmosphere.
One of geothermal energy's major benefits is its capacity to produce a steady stream of electricity, sometimes known as baseload power. Because geothermal plants can generate power continuously, they can provide a consistent energy production independent of external influences, unlike solar or wind energy, which can be erratic owing to weather. When operating, geothermal energy emits very little greenhouse gas when compared to fossil fuels. Due to its ability to fulfill expanding energy demands responsibly, it is an environmentally benign choice that provides a substantial contribution to lowering carbon footprints. Reaching long-term renewable energy targets while fostering ecological balance can be accomplished by harnessing Earth's heat.
Being a renewable energy source that is both flexible and sustainable, biomass energy comes from organic materials. Wood and agricultural residues are common sources of biomass, as is municipal solid waste. Straw, corn stalks, and sugarcane bagasse are examples of agricultural waste that has a lot of potential for energy production. Historically, wood has been the main biomass fuel used for cooking and heating. A number of methods exist for turning livestock waste into energy. Biomass is a renewable energy source that can be used to manage waste effectively by utilizing these materials.
A number of processes are involved in converting biomass into useable energy. The most popular technique is combustion, which involves burning organic materials to create heat that can be used to warm homes or businesses or to supply direct thermal energy. An additional method that shows promise is anaerobic digestion, which breaks down organic waste without the presence of oxygen and produces biogas, which is mainly made up of carbon dioxide and methane. In order to convert this biogas into biomethane, which may be utilized as fuel for cars or in natural gas networks, it can either be used straight for heating or electricity production.
Its capacity to decrease waste while offering a renewable fuel source is one of biomass energy's main benefits. Biomass supports more environmentally friendly methods of waste management by making use of organic waste and agricultural residues that would otherwise break down in landfills and release greenhouse gasses like methane. The carbon dioxide emitted during combustion of biomass is about equal to the quantity absorbed by plants during their growth cycle, meaning that biomass has the potential to be carbon neutral. With regard to attempts to reduce climate change and promote environmental sustainability, this feature makes biomass a desirable alternative.
A special chance exists to turn organic waste into useful fuel resources through the use of biomass energy. Significant advantages like waste reduction and potential carbon neutrality are provided by its varied sources and conversion techniques, which also emphasize its adaptability as an energy solution. Biomass could become a more important component of our shift to greener energy systems as technology develops and public awareness of sustainable practices increases.
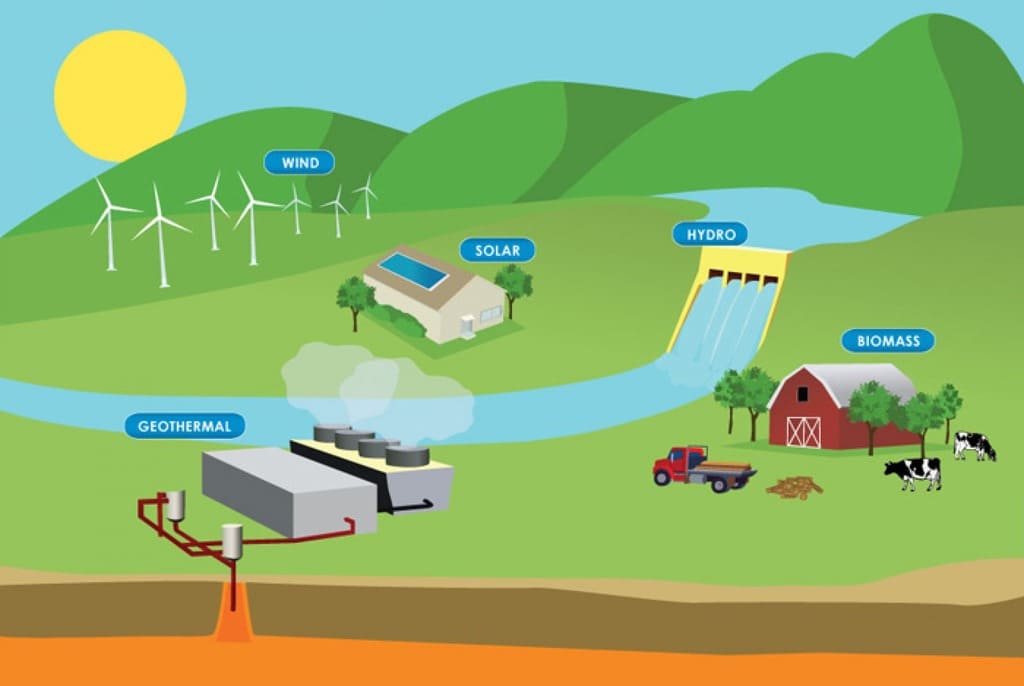
Efficiency, affordability, and environmental impact are highlighted as three critical variables that must be compared when assessing renewable energy sources. Every renewable energy source, including biomass, geothermal, hydropower, solar, and wind, has distinct benefits and drawbacks that can have a big impact on how widely used and adopted they are.
When assessing how well an energy source transforms raw materials into usable electricity, Efficiency is a crucial consideration. Depending on developments in technology, solar panels can have an efficiency rate of anywhere from 15% to 22%. Though hydroelectric systems frequently achieve efficiencies above 90% because they directly convert kinetic energy from flowing water, wind turbines can only attain efficiencies of about 35% to 45%. Although they have limited geographic availability, geothermal plants also have high efficiency rates. While it is not as efficient as these other sources, biomass is remarkable in how well it can use waste materials. 🎚
The viability of initiatives involving renewable energy is heavily influenced by Cost. Solar energy has become increasingly affordable for both homeowners and companies in the last ten years, thanks to a significant decline in the initial investment required. Economic benefits and technological advancements have also resulted in lower costs for wind energy. While hydroelectric projects often result in cheap operating costs over time, they do require a significant upfront capital investment during construction. After installation, geothermal systems have lower fuel costs, which means they can provide steady long-term profits. While it may have greater processing costs, biomass is nevertheless competitive in some areas where agricultural waste is plentiful.
With each renewable source, there are significant differences in the environmental impact. Even though the production of solar and wind turbines entails the exploitation of resources, these energy sources produce electricity without emitting any emissions when in use. Though they emit very little greenhouse gas when in operation, hydroelectric facilities have the potential to upset local ecosystems through the damming of rivers. A tiny carbon footprint is associated with geothermal energy, but improper management can result in water contamination or ground subsidence. Though unsustainable procurement techniques can offset the environmental benefits of biomass, it nevertheless makes use of organic materials that would otherwise go to waste.
When compared to these crucial criteria, every renewable energy source has unique advantages and disadvantages. Whereas geothermal power gives steady baseload electricity and is consistently cheaper than solar power, wind power is more efficient than solar, hydroelectric power is dependable, and biomass is versatile but poses a risk to the environment if not managed responsibly. Stakeholders seeking to apply efficient renewable solutions customized to particular requirements and settings must have a thorough awareness of these characteristics.
As a major contributor to the global energy goals, renewable energy is essential to the advancement of sustainable development. Biomass, solar, wind, hydropower, and other renewable energy sources offer greener substitutes for fossil fuels as nations work to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and address climate change. Relying on these sustainable energy systems would allow countries to fulfill their obligations under global accords such as the Paris Accord while guaranteeing increased energy access for all people. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially Goal 7, which calls for universal access to cheap, clean energy, are in line with this change in addition to addressing environmental issues.
Renewably produced energy has significant economic benefits in addition to positive environmental effects. Growing recognition is being given to the sector's ability to boost local economies and generate jobs. Creating jobs at all levels, from production and installation to maintenance and operation, is a common result of investing in renewable technology. By means of local supply chains and services related to these technologies, communities that adopt renewable projects can witness a rise in GDP. Reducing dependency on foreign fuels allows nations to maintain financial resources domestically while improving energy security.
Community development is yet another crucial facet of the renewable energy environment. By including communities in the decision-making process about their energy needs, many local renewable projects strengthen the communities in which they are implemented. With regard to energy costs or supply disruptions, for example, this participative approach strengthens social cohesion and increases resilience against external shocks. In order to improve quality of life by facilitating improved access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities, decentralized renewable energy systems, such solar microgrids, can supply electricity to isolated places that regular grids could miss.
It is not only ecologically sustainable but also fosters economic development and community empowerment when renewable energy is incorporated into national strategies. Exploiting renewable energy to its fullest will be crucial to creating a future that is more resilient for the earth and its inhabitants as long as sustainable development remains a top priority worldwide.
Though there are a number of major obstacles preventing its mainstream acceptance, the switch to renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable future. In order for legislators, business executives, and the general public to collaborate on finding answers, it is imperative that they comprehend these challenges.
Technological Barriers
Renewable technologies are developing quickly, but their widespread adoption is still hampered by a number of technological obstacles. The field of energy storage technologies, for example, is still in its infancy. Although batteries have made great strides, large-scale costs and efficiency issues still plague them. Because solar and wind power are highly dependent on the weather, integrating renewable energy sources into the current grid infrastructures can be challenging. In order to guarantee a consistent supply of electricity, this intermittency calls for complex control systems and backup supplies.
Policy and Regulatory Hurdles
The legal and regulatory structures controlling the production of energy present another significant obstacle. Outdated restrictions create an unequal playing field in many locations by favoring fossil fuels over renewables. Market distortions may arise from the inadequacy or uneven application of incentives, such as tax credits or subsidies, across various technologies. Approvals for projects can be delayed and developer expenses raised by bureaucratic procedures. To promote a more equal transition, effective policies must develop to actively support renewable technology while phasing out fossil fuel incentives.
Public Perception Issues
The way that the public views renewable energy sources is crucial to their uptake. Though misconceptions over renewable technologies have persisted, knowledge of climate change has considerably expanded in recent years. Without realizing the long-term savings and environmental benefits, some people could think renewable energy sources are costly or unreliable. Concerns regarding land use or the aesthetic impact of projects like solar arrays or wind farms might give rise to local opposition. Campaigns for comprehensive education that convey the financial and environmental advantages of switching to cleaner energy sources are necessary to overcome these perception problems.
In order to address these issues and establish an atmosphere that supports the expansion of renewable energy, communities, corporations, and governments must work together. A more sustainable future driven by clean energy can be achieved by making investments in technology development, changing laws, and raising public awareness.
Notable developments in the renewable energy space hold out the possibility of improving accessibility and efficiency. Leading the charge with notable improvements in performance and cost-effectiveness are recent developments in solar panels and wind turbines. Bifurcated solar panels, for example, have changed the game by producing more electricity without requiring more land. They do this by capturing sunlight from both directions. Perovskite solar cells give higher efficiency rates and cheaper production costs than conventional silicon-based panels, thanks to developments in materials science.
Significant advancements in wind energy technology have also occurred. Modern wind turbines are able to capture stronger winds at higher altitudes because of their bigger blades and longer towers. The cost per megawatt-hour produced is decreased in addition to increasing the amount of electricity generated by these advancements. With the increasing popularity of floating wind farms, offshore wind energy production now has more options for producing wind energy due to the ability to deploy turbines in deeper waters with stronger and more constant winds.
Diverse renewable energy horizons are represented by emerging technologies such as wave and tidal power. The moon and sun's gravitational pull on Earth's seas is harnessed by tidal power, and surface waves' kinetic energy is captured by wave energy. Regarding dependable and predictable renewable energy sources with little to no environmental impact, both approaches hold out a lot of promise. Improvements in efficiency and lower costs are anticipated as research into these technologies progresses, which may enable them to compete with more established renewable energy sources.
Trends in renewable energy for the future point to a move toward further integration of decentralized systems and smart technologies. Renewable energy systems are being maintained more efficiently and with better predictive maintenance because to innovations like artificial intelligence (AI) and grid management. The solution to the intermittent problems with solar and wind power will largely depend on developments in battery storage technology. With the development of these advances, renewable energy will become more viable while simultaneously easing the world's transition to a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
Future cleaner energy is being ushered in by ongoing advancements in a variety of renewable energy technology domains. We can expect a broad range of options for sustainably fulfilling our expanding energy demands as new technologies like tidal and wave energy are developed alongside ongoing advances in established solutions like solar panels and wind turbines.
Nations with effective renewable energy deployments that are useful case studies for the international community include Denmark and Germany. In addition to making significant investments in renewable technology, these countries have created extensive structures and laws that support sustainability and innovation.
One of the main factors in changing Germany's energy environment is the Energiewende (energy transition) initiative. Through the promotion of wind, solar, and biomass energy, Germany has managed to raise its proportion of renewable energy to more than 40% of all electricity generated. The North Sea offshore wind farms are one noteworthy project that has established industry standards for productivity and efficiency. Germany's approach has taught us valuable lessons about the significance of public involvement, robust regulations, and government incentives in promoting long-term investments in clean energy.
The ambitious ambition of Denmark to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 sets them apart. By making large expenditures in wind energy, both offshore and onshore, the nation has advanced significantly. An example of how large-scale projects may efficiently utilize natural resources and reliably power millions is the Horns Rev offshore wind farm, one of the largest in the world. In addition to highlighting the importance of strong grid infrastructure to handle growing percentages of intermittent energy sources, Denmark's experience highlights the vital role that local communities play in promoting renewable projects.
These nations demonstrate the need for a multidimensional strategy that includes community involvement, policy backing, and technological innovation for the successful use of renewable energy. Other countries looking to shift to sustainable energy systems can benefit from the lessons learned from Germany's and Denmark's experiences. Three important lessons to be learned are to prioritize R&D, ensure flexible market structures that can adjust to changing technologies, and promote cooperation between public and commercial sectors as well as citizens.
These case studies show that significant advancements in the use of renewable energy may be made while successfully addressing climate change challenges, provided that initiative and strategic planning are put into place.
The prospects for renewable energy seem extremely bright when we look ahead. Over the next ten years, predictions suggest that industries like hydropower, solar, and wind power will all continue to grow dramatically. Diverse industry assessments anticipate that by 2025, worldwide expenditures in renewable energy will eclipse those in conventional fossil fuels due to breakthroughs in technology and declining expenses. This move underscores the potential of renewables for job development and economic growth, in addition to reflecting a rising appreciation of their environmental benefits. 🫣
Securing strong policy support from governments across the globe is necessary to realize this promise, though. To speed up the move away from fossil fuels, effective policies that provide incentives for the development and use of clean energy are necessary. Policy frameworks that support renewable technology R&D and offer financial incentives to producers and consumers alike must be put in place by the government. A stable market environment that prevents the fossil fuel industry's subsidies from overshadowing the renewable energy sector is something that these kinds of policies can contribute to.
Educating the people on the advantages of renewable energy is equally vital. The public will demand cleaner energy solutions as they become more aware of the effects of climate change and the benefits of sustainable activities. Public awareness campaigns on renewable energy sources have the potential to inspire grassroots movements that support regional projects, thereby exerting additional pressure on decision-makers to give priority to sustainable projects.
From all of the above, we can infer that even though there are still obstacles in the way of achieving a completely renewable energy landscape, the direction is evident: in the years to come, we can anticipate a major shift in the way we produce and use energy thanks to sustained investment, encouraging legislation, and growing public awareness. Accepting this shift opens the door to creative economic prospects that benefit society at large, in addition to making the world healthier.
post 3
Я с вами полностью согласен!
post 2
Я полностью с вами согласен👌
text 6
Это правда!
title 4
Fantastic tips, as always!
Types of renewable energy their comparison and main advantages
What an absolutely informative article! Everything I needed to know is here, plus a lot of stuff I didn't know I needed to know. Fantastic job, I can't thank you enough or praise you more highly, and I'm not normally prone to write comments
post 3
Excellent information! I love how you laid it out step by step. Great job!
post 2
Another great article, David
post 3
Thanks for this, it's useful to get information collated that covers the whole process rather that the many detailed guides that cover any single stage🧐
Types of renewable energy their comparison and main advantages
What an absolutely informative article! Everything I needed to know is here, plus a lot of stuff I didn't know I needed to know. Fantastic job, I can't thank you enough or praise you more highly, and I'm not normally prone to write comments 😍